KIT at Hannover Messe 2025
Intelligent wearable for the ear based on an open-source platform, cooling methods that do not require the use of refrigerants as well as optical nanostructured surfaces, for example for new types of cameras, are among the top topics of KIT in the Future Hub (Hall 2, Stand B35). Also: efficient energy management for large-scale research and projects of the student group Engineers Without Borders for sustainable developments worldwide.
At Energy Solutions (Hall 13, Booth C76), the focus is on electrical energy supply: Here, the KIT will present a modular battery storage system, multifunctional organic solar cells for agricultural and urban applications, an energy management system and research into the direct recycling of functional materials from lithium-ion batteries.
Future Hub
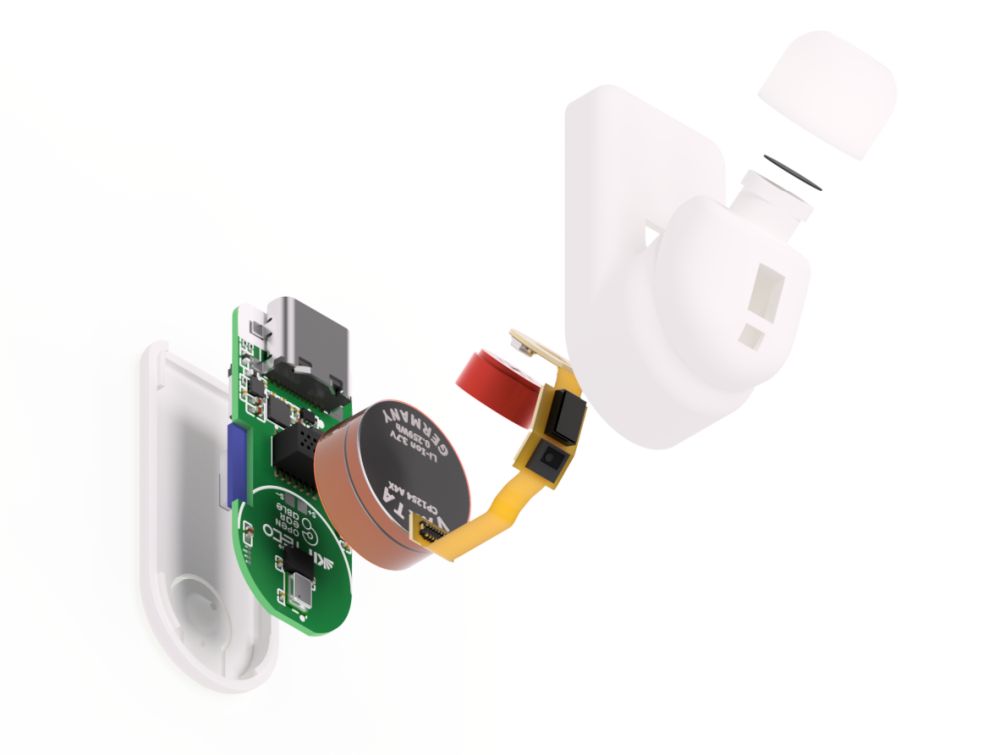
OpenEarable: Open-Source AI Ear Sensing Platform
OpenEarable is a open-source AI platform developed at KIT that transforms wireless earphones from mere audio devices into next-generation smart wearables. Featuring the most extensive array of sensors ever integrated into earphones, OpenEarable revolutionize communication in noisy environments, enhance work health and safety, and provide AI-powered operation that leaves hands and eyes free.
Equipped with three microphones per ear, OpenEarable delivers crystal-clear communication by capturing speech through vibrations in the user’s skull, ensuring clarity even in the loudest industrial settings. Motion sensors enable precise fall detection and monitoring of repetitive movements, while advanced biosensors safeguard workers by detecting fatigue, heat stroke, and other health indicators — even under the most demanding conditions.
OpenEarable empower developers to create bespoke software applications that run directly on the device. Complementing this versatility, a dedicated mobile app and web dashboard enable users to drive innovation and tailor solutions to diverse use cases.
ZEco Thermal Lab: Sustainable Cooling and Heating
ZEco Thermal Lab develops cooling and heating technologies for a variety of applications ranging from micro cooling of electronics to large-scale air conditioning. The technologies rely on solid-based cooling using the so-called elastocaloric effect: Certain materials heat up and cool down under mechanical loading and deloading. In this way, it is possible to directly convert mechanical into thermal energy without needing media such as gases or liquids. The technologies by ZEco Thermal Lab are emission-free and highly sustainable.
KITTEN: Test Field for Energy Efficiency in Large Research Infrastructures
To enhance the energy efficiency and sustainability of large research infrastructures, in particular particle accelerators, KIT has established the KITTEN test field. It combines physics and energy technology to develop and test multidisciplinary solutions from the component level to the system level. The results will also benefit other energy-intensive infrastructures, such as computing centers, hospitals, and plants of steel or chemical industries.
Optical Metasurfaces for Compact and Multifunctional Optical Components
Minute nanostructures can manipulate light. Specifically designed nanostructured layers are used to produce lightweight, compact, and multifunctional optical components. These can be applied to focus light and to generate structured light and holograms. It is even possible to replace several optical elements by a single optical meta surface. Production of such meta optics is compatible with standard processes to manufacture semiconductors and, hence, suited for mass production.
Engineers Without Borders (EWB): Development Cooperation Projects
An example of the outstanding commitment of students at KIT: For 20 years now, Engineers Without Borders, a group of students from KIT, have carried out various engineering projects in economically, socially, or politically disadvantaged regions in order to create new perspectives for the population there. So far, a total of 1,500 members have implemented nearly 40 projects in 13 countries and collected donations in the total amount of EUR 2.5 million. Their projects focus on education, water supply, energy supply, healthcare, and infrastructure. KIT supports EWB with knowledge, advice, and inspiration.
Energy Solutions
RAZO: Smart Interconnection and Control of Devices
The RAZO energy management system enhances the use of renewable energies and supports consumers of electrical energy, who also produce electricity, in optimizing their costs. Using RAZO, electric vehicles, batteries, and heat pumps can be interconnected and controlled smartly. Prosumers can optimally use their excessive photovoltaic energy and purchase additional power when it is cheapest. RAZO’s current pilot experiment covers a virtual power plant that integrates various decentralized energy resources.
Rethinking Photovoltaics: Double Use of Spaces and Organic Solar Cells
Use of solar energy can be combined with agricultural areas, facades of buildings, or other sealed areas. An example is the integration of photovoltaic elements in the outer walls of greenhouses. Organic solar cells are particularly suited for integration in widely used infrastructures and inexpensive mass production. KIT has developed highly specialized and environmentally friendly semiconducting inks for the production of organic solar cells from water or alcohol and operates an automated research platform that combines ink synthesis, layer deposition, and characterization.
LeMoStore: Inverter and Energy Storage System Combined
To integrate renewable energies in the grid, inverters and storage systems are needed. LeMoStore (lifetime-optimized modular energy storage system) combines both functions. The integrated battery modules do not have to be identical in construction. It is also possible to apply spent batteries of different designs. Strategic division of charge and discharge power allows for the optimization of battery lifetime and the reduction of installed storage capacity. In this way, economically efficient and sustainable systems can be implemented.
DiRecFM: Direct Recycling of Battery Electrodes
In view of the scarcity of metals, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are used in lithium-ion batteries, efficient concepts for recycling are in high demand. Direct recycling of battery electrodes is highly sustainable. By means of gentle processes, active materials are recovered while maintaining their functions and then directly fed back into battery production. KIT will present a mechatronic concept for the mechanical removal of the active anode material from the copper foil by brushing.
Further Booths
The Center for Electrochemical Energy Storage Ulm & Karlsruhe (CELEST) will present its work at the stand of Baden-Württemberg international (Hall 13, Stand C78). CELEST offers a big platform for scientific collaboration and technology transfer in the area of electrochemical energy storage (EES), from fundamental research to the manufacture and testing of large cells. The platform combines the know-how of its partner institutions, namely, KIT, Ulm University, and the Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg. Research of the CELEST members covers lithium and post-lithium batteries as well as alternative electrochemical energy storage and conversion systems, in particular hydrogen and fuel cells.
With their vision of sustainable and zero-emission future mobility, KIT and the University of Stuttgart established their joint research platform Innovation Campus Future Mobility (ICM). ICM will also present its AI-supported inspection system for electronic products at the stand of Baden-Württemberg international (Hall 13, Stand C78). The system helps to optimize the reuse of printed circuit boards, as it pools various inspection methods, evaluates results in real time, and specifically initiates repair, reuse, or recycling measures. In this way, it contributes to a resource-efficient and profitable circular economy. ICM will also present its miniaturized vehicle Mini-eVee, a platform to test new communication, control, and driving concepts.
KIT-Gründerschmiede (KIT Founders Forge) is one of the biggest university-based startup centers in Germany. It pools KIT’s startup and entrepreneurial activities. Together with ten startups from KIT, the KIT Founders Forge will present itself in the Start-up Area (Hall 2, Stand D26). Every day, two startups will be showcased and they will pitch on the Industrial Startup Stage: adjusted flow GmbH and FastCast GmbH, PrioOptics GmbH and Validaitor GmbH, Desoltik and KCM – Karlsruhe Conductive Materials, Spotium GmbH and NextStepHR GbR, Avo Labs Inc. and Catavis.
Conference Program
Tech Transfer Conference Stage (Halle 2, Stand B02)
Monday, March 31, 2025, 15.15 hrs
Keynote: Science for Impact
Professor Thomas Hirth, KIT Vice President Transfer and International Affairs
Monday, March 31, 2025, 16.30 hrs
Panel Discussion: Night of Innovations "Future energy"
Holger Lösch, Bundesverband der Deutschen Industrie e.V, Prof. Dr. Sibylle Günter, Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Professor Dr. Veit Hagenmeyer, Institut für Automation und angewandte Informatik des KIT, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Holger Hanselka, Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Christina von Saß, NDR
Wednesday, April 02, 2025, 13.50 hrs
Presentation: Revolutionary Lightweight and Compact Optical Metagrating: 4x Efficiency Boost at High Angles
Dr. Maryna Meretska, Institute of Nanotechnology of KIT
Wednesday, April 02, 2025, 14.15 hrs
Presentation: Elastocaloric Technology: Pioneering Sustainable Cooling and Heating Solutions for a Greener Future
Dr. Jingyuan Xu, Institute of Microstructure Technology of KIT
Convention Center
Tuesday, April 01, 2025, 13.00 hrs
Event: INNO-Bat – Innovative Approaches in Battery Technology
Center for Electrochemical Energy Storage Ulm & Karlsruhe (CELEST)

Project Manager Trade Fair, Congress, Event
Campus Services
+49 721 608-29202